Country Selector
Our Propyzamide Knowledge Hub has been created for oilseed rape growers and advisors. The new materials go back to basics on what propyzamide is, how it works, how to apply it to achieve the best outcome, and practical advice on how to use it responsibly.
What is propyzamide?
Propyzamide is a selective, systemic herbicide for use in oilseed rape. It controls key grass weeds such as blackgrass and ryegrass which are resistant to alternative chemistry.
There is no known resistance in Europe to propyzamide which makes it a key tool to help manage and reduce the burden of these weeds across the rotation.
Renowned herbicides such as Astrokerb® and Kerb® Flo 500 contain propyzamide and are the cornerstones of many herbicide programmes.
- Propyzamide is a selective, systemic, pre-emergence, and/or early post-emergence herbicide used for control of annual and perennial grasses and certain broadleaved weeds.
- It is a soil active systemic herbicide.
- Its major use is in oilseed rape. It can also be used in a number of other crops which you can view by going to the product pages – Kerb Flo®, Kerb Flo 500, Astrokerb
- Active ingredient
- Application
- Water stewardship
- CPD Quiz
About the active ingredient
1. Mode of action
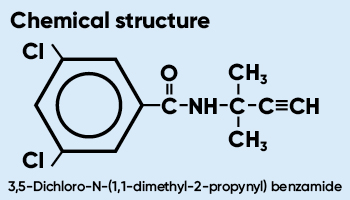
Propyzamide (Pronamide) is the common name for: 3,5-Dichloro-N-(1,1-dimethyl-2-propynyl) benzamide.
It is a member of the amide or substituted amide chemical family (sometimes referred to as benzamide family of chemistry).
Propyzamide acts by preventing plant cell division. It inhibits mitosis by binding to tubulin and preventing its assembly into microtubules.
It has herbicide Mode of Action Classification - Group 3.
Primarily root uptake and upward translocation.
2. How it works
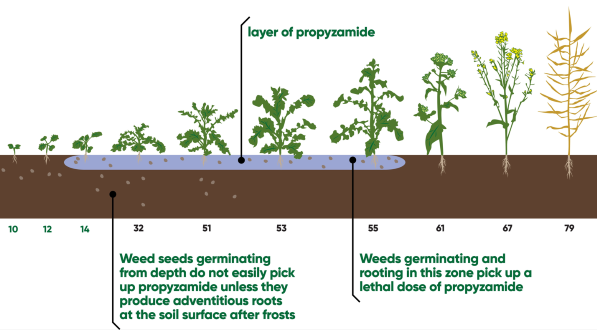
Propyzamide must move into the soil root zone for effective contact with plant roots.
Propyzamide is primarily translocated upwards in plants following root absorption.
By forming a chemical layer in the upper soil zone, propyzamide affects plants through root absorption (direct contact at germination and/or emergence).
Because of the length of soil persistence, soil activity may last up to three months.
Improved efficacy in frosty conditions
In frosty conditions and in response to frost heave, plants such as blackgrass may produce adventitious roots.
These rootlets absorb propyzamide from the surface layers of soil. Under these conditions, despite plants being well established and deeply rooted, excellent control can be achieved.
3. Products and weeds controlled
Grass weeds: Blackgrass, ryegrass, annual meadow-grass, barren brome, volunteer cereals, wild oats.
Broad leaved weeds: Common chickweed, black bindweed, black nightshade, fat-hen, redshank, small nettle, speedwell, forget-me-not, knotgrass.

1. How to apply propyzamide - best use for blackgrass control
It is important to get a good residual layer for robust control. It’s a balance – the conditions need to be right – but if you wait too long and the blackgrass plants are too big it can give poorer results.
Use Kerb Weather Data to keep track of the best time to apply. Sign up to our Kerb Weather Data e-newsletter and receive autumn application advice on soil temperatures to support optimum timing of Kerb & Astrokerb.
Check out our topic sheet which gives you the latest Advice on blackgrass control in oilseed rape.
Right RATE
Assess black grass population and select appropriate dose rate.
750g ai/ha good control.
840g ai/ha gives more robust control especially in heavy blackgrass populations.
Right CONDITIONS
Apply when soil temperatures are declining and there is sufficient moisture.
Optimum temperature is 10ºC and declining at 30 cm of soil
Adequate soil moisture is essential to move the chemical into the root zone of weeds
Right TIME
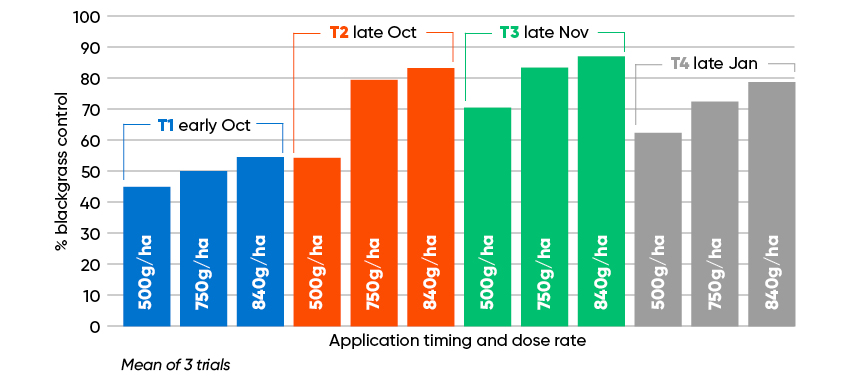
Trials have shown the best time to apply tends to be end Oct-November because this is the time where soil temperatures are falling and are ideal for propyzamide application.
2. When to apply propyzamide for optimum blackgrass control
Trials looked at timings, rates and soil temperatures for the most effective control of blackgrass with propyzamide.
- Applications made in late October to early December are most effective.
- September and early October applications are too early and January applications are too late.
- Key parameter is soil temperature must be falling, use Kerb weather data.
- 840gai/ha of propyzamide is required in heavy blackgrass situations.
- 500gai/ha of propyzamide is insufficient where blackgrass is a serious threat.
3. Kerb Weather Data
The Kerb Weather Data (KWD) tool is meant to be used as a guide to local weather conditions. It can aid growers and advisors in making local tactical decisions to optimise their Astrokerb® and Kerb® Flo 500 applications and thus their activity against blackgrass. It is based on the traffic light system to help farmers optimise their application timings.
For Kerb Weather Data with advanced functionality, download the free Corteva Arable App.
4. Symptoms


Water stewardship
After a heavy rain event there is a risk of propyzamide attached to soil particles getting washed into surface water. Appropriate planning, management and adoption of stewardship practices must be followed to mitigate this risk.
Go to our propyzamide stewardship page to read more about guidelines and practices to follow.
CPD courses and quizzes
Let’s test your knowledge about propyzamide.
After reviewing the materials on this hub and our stewardship page, head over to the CPD quiz page to test your knowledge.
Earn CPD points. BASIS points: 3 (1 CP; 1 E; 1 AP) and 3 NRoSO points.
Interested in earning more CPD points?
Check out the BASIS Classroom course that launched in September 2024: IPM: Managing Arable Weeds. 
Other useful information
- Advice for blackgrass control in oilseed rape - download the topic sheet here.
- Herbicide programmes for oilseed rape - download the topic sheet here.
- Astrokerb and Kerb Flo 500 application advice, available as a downloadable leaflet. It contains links to key information and stewardship resources. To request leaflets email: events@corteva.com.
Contact us
If you would like to contact a member of the team, click here to find your local area manager.
Alternatively, you can call our Technical Hotline on 0800 689 8899, email ukhotline@corteva.com, or complete our enquiry form.